All about Lithium batteries and their applications for EV vehicles
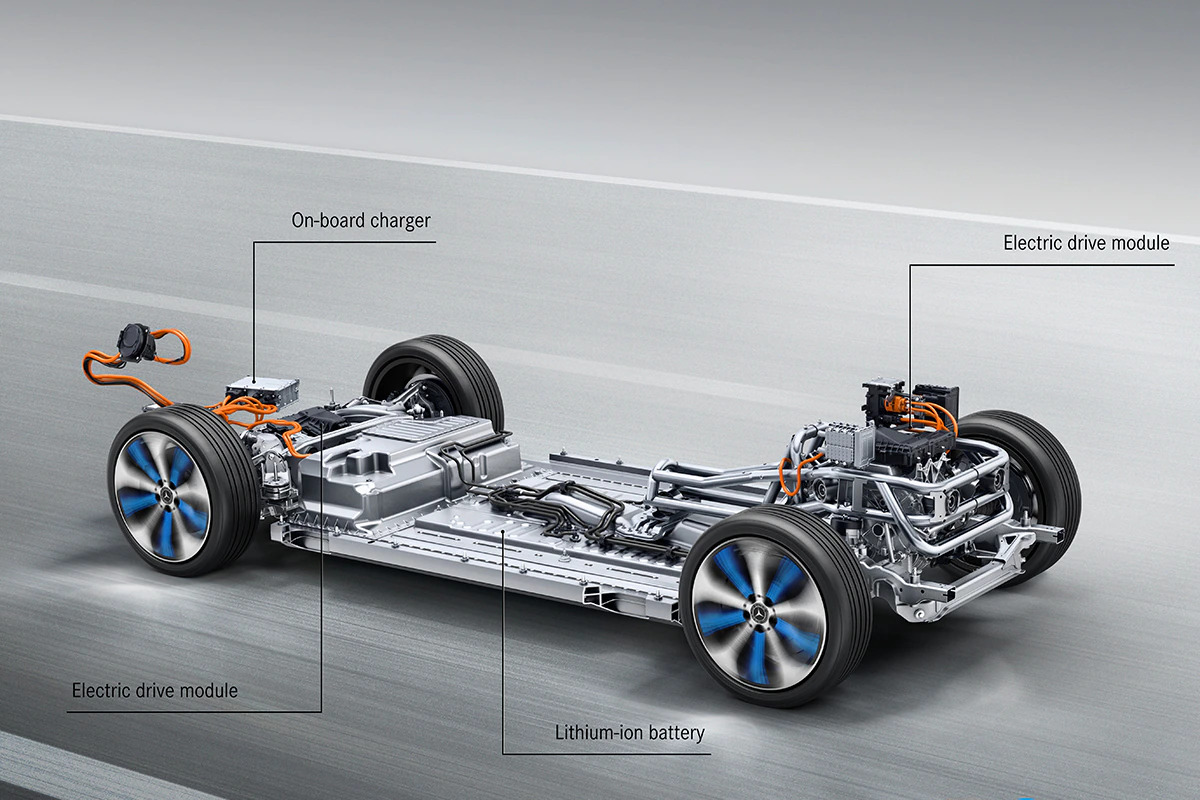
There has been a substantial rise in the adoption of green and renewable energy for various consumption. One of the most successful aspects of green energy consumption is electric vehicles (EVs). The world has been moving rapidly towards mobility transition. And this has led to a sudden rise in demand and consumption of batteries across the globe. A study by Global Market Insight projected that the Lithium-Ion battery market is going to expand by more than 16% from 2023 to 2032. Consumer preference for EVs and Hybrid Vehicles is driving the demand for lithium batteries. Moreover, the market value of the lithium-ion battery sector is set to rise from $ 48.19 billion in 2022 to $ 182.33 billion in 2030, with a CAGR growth of 18.2%. Are you planning to get your first EV? Are you worried about the batteries used? If yes, you have landed at the right place. Let us learn and understand the various batteries that can be used and applied in Electric Vehicles. In general terms, a battery has three parts to generate electricity. Anode- Negative point of the battery Cathode- Positive point of the battery Electrolyte- chemical pasting that separates anode and cathode, transforming chemical energy into electrical energy. Over 60% of the battery is made of materials like manganese (Cathode), zinc (Anode), and Potassium. Lithium-ion batteries use interchanged lithium compounds like graphite as the negative electrode and positive electrode. Introduction
What is a Battery Chemistry?
As simply put, Electric Vehicles are powered by an electric battery. There are different types of batteries used in EVs. Among the listed battery list, lithium-ion batteries are the most efficient and popular amongst EVs. Here are the various batteries used in Electric Vehicles. Lead-Acid Batteries- Some of the benefits of lead-acid batteries are that they have high power, are less expensive, reliable and safe. This type of battery is used in commercial vehicle that runs on ancillary roads. Drawbacks of this battery type are low energy, poor temperature, and short cycle life. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries- This battery type has a longer life cycle, is very safe and reliant and is most commonly used in hybrid vehicles. Some of the challenges faced in Nickle-Metal Hydride Batteries are high self-discharge ratio, high cost, and controlling of hydrogen loss. Lithium-Ion Batteries- lithium-ion batteries are popularly used in EVs because of their high energy per unit mass. They also have high energy efficiency, high-temperature performance, high power-to-weight ratio, and slow self-discharging capability. These lithium batteries vary according to their chemistries based on metal oxide cathode and anode reactions. Nickle Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) are the two most commonly used lithium batteries. These batteries are used in EVs, residential batteries and so on. Sodium-ion Batteries- Sodium-ion batteries are still in the evolving phase and are being considered as a prospective substitute for lithium-ion batteries. Some of the main benefits of sodium-ion-based batteries are they are available in abundance and at a reasonable cost. They are non-flammable and highly energy dense and can withstand cold temperatures. One backdrop of sodium-ion batteries is that they lack durability. Lithium metal Batteries- Lithium-metal batteries have been under-development since 2007, and the existing batteries are mostly non-rechargeable. Studies are still being conducted to make lithium metal batteries rechargeable and efficient. These batteries generally cost high per unit and have a very high energy density. Solid State Batteries- Solid state battery consists of a cathode composite layer, carbon-free micro silicon anode and a sulphide solid electrolyte layer. A lithium-ion battery is in a liquid state, and a solid-state battery is in a solid state. The benefits of solid-state batteries are that they offer a higher range, are lighter, recharge faster and have a high energy density. From the above information, we can say that demand for lithium-ion batteries is set to rise at an exponential rate in the coming next decade. Batteries have many applications, but batteries use in Electric vehicles (EVs) is very high. From all the battery types like Nickle-Metal Hydride, Solid state, Lead-Acid, and Ultraceptors, Lithium-Ion battery is the most common and efficient form of battery used in EVs. The main components of a typical electric battery are Anode, Cathode and Electrolyte. These chemical exchanges transform into electrical energy. Some of the raw materials used in a battery are Cobalt, Graphite, manganese, Nickle and lithium. Similar to ICE vehicles, EVs depend on factors like speed, traction, load and wind. Conclusion